In the pursuit of optimal health and choosing a supplement, understanding the intricacies of our body's inner workings is essential. One such critical component is NADH, short for Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Hydride (NADH), also known as the B vitamin, B3 or Niacin.
In this blog, we will delve into what NADH is, why it is crucial for our health, its roles in the body, and why choosing Dr. Tennant’s® Restore will provide you with the most bioavailable and methylated NADH (Vitamin B3) compared to other supplements.
WHAT IS NADH?
NADH, is a bioavailable form of Vitamin B3. It serves as a vital cofactor in cellular respiration—a complex process that powers our cells and generates energy from the food we consume. NADH is a versatile molecule with a central role in various cellular activities, making it an essential part of our overall health.
Here are just a few critical roles NADH plays in our health:
How Does NADH Work in the Body?
NADH serves as a critical co-factor in energy production. It acts as an electron carrier during glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, accepting electrons from glucose molecules and transferring them to other molecules. This electron transfer is pivotal for the synthesis of ATP, providing the energy needed for various metabolic processes.
In addition to its role in energy metabolism, NADH participates in numerous cell redox reactions, acting as an electron transporter. These redox reactions are fundamental to various metabolic pathways, including glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. By facilitating the transfer of electrons, NADH helps restore cellular balance and promotes ATP production.
The Importance of NADH in Cellular Energy Production
NADH's role in cellular energy production cannot be overstated. It acts as a critical player in the electron transport chain, a central component of cellular respiration. During this process, NADH donates electrons to the chain, ultimately leading to the generation of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate), the primary energy currency of the cell. This energy is vital for powering various cellular functions, including muscle contraction, nerve signaling, and maintaining body temperature.
In addition to its role in energy production, NADH is also a key player in the methylation cycle, which is a fundamental biochemical pathway in the body. This cycle is responsible for processes such as DNA and RNA synthesis, detoxification, and neurotransmitter production. NADH's involvement in the methylation cycle underscores its importance in cellular health.
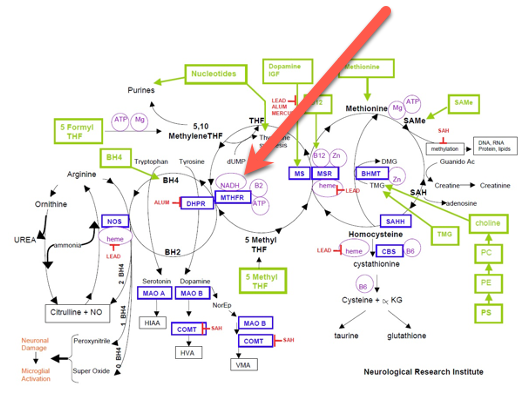
(Methylation Cycle that our bodies perform millions of times a day.)
What is the Difference Between NAD+ and NADH?
NADH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Hydride) is a coenzyme that plays a crucial role in various metabolic processes within cells. It is derived from vitamin B3, also known as niacin, and exists in two forms: NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) and NADH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Hydride).
Understanding the difference between these two forms is essential in recognizing why choosing NADH over NAD+ is important for overall health.
What is NAD+? (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide)
-
Oxidized Form: NAD+ is the oxidized form of the coenzyme. In other words, it has lost electrons during a chemical reaction.
-
Electron Carrier: NAD+ primarily functions as an electron carrier. It accepts electrons from molecules being oxidized (losing electrons) during metabolic reactions.
-
Low Energy State: NAD+ is in a lower energy state because it lacks the extra electrons that NADH carries.
- Participates in Catabolic Reactions: NAD+ is involved in catabolic reactions, such as glycolysis and the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), where it helps extract energy from nutrients like glucose.
What is NADH? (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Hydride)
-
Reduced Form: NADH is the reduced form of the coenzyme. It carries extra electrons, making it a high-energy molecule.
-
Electron Donor: NADH functions as an electron donor. It provides electrons to other molecules during metabolic reactions.
-
High Energy State: NADH is in a high-energy state due to the electrons it carries, which are potential sources of energy for the cell.
- Participates in Anabolic Reactions: NADH is involved in anabolic reactions, such as the synthesis of molecules like fatty acids and nucleotides, where it provides the necessary reducing power for these biosynthetic processes.
Choosing a supplement with NADH vs NAD+ is important, because: NADH is further broken down, is further down the methylation cycle, and is more readily used by the body.
Bioavailability Matters
Just like other nutrients and coenzymes, the bioavailability of NADH is crucial. High-quality supplements aim to provide NADH in a form that the body can readily absorb and utilize. This approach reduces the need for additional conversion steps, ensuring that NADH can efficiently support energy production and cellular processes.
Individuals who may experience difficulties with methylation due to genetic factors or other issues can benefit from supplements containing NADH, among other methyl donors. These supplements can help address methylation challenges and potentially improve overall health.
IN SUMMARY
NADH, as the reduced form of NAD+, is a vital coenzyme in the body, playing a crucial role in cellular energy production, redox reactions, and the methylation cycle. Choosing bioavailable NADH over NAD+ simplifies the body's utilization of this essential coenzyme, supporting efficient metabolic processes and contributing to optimal well-being. When considering supplements or nutritional choices, prioritizing NADH can be a valuable step toward promoting your health and vitality.
Let’s Wrap It Up…Where Can I Get NADH
We know this is a very complicated process to understand but the biggest take away we want you to have is that NADH is a powerhouse vitamin that plays a pivotal role in our body's energy production and overall health. By choosing Dr. Tennant’s® Restore, you're making a proactive decision to support your cellular energetics and optimal health. Its ability to enhance NADH levels, act as a biological antioxidant, and address various aspects of health, makes it a valuable addition to your wellness regimen to help you achieve optimum health.
Want to learn more about Dr. Tennant's® Restore Formula NADH ingredeint? Click here to read about PANMOL® NADH.
Remember, when it comes to your health, informed choices can make a significant difference.
It’s your body. It’s your life. Ingredients matter.
Featured Products in This Article:

Dr. Tennant’s® Restore
An all-natural, biologically active formula. Restore contains superior quality ingredients in the most bioavailable form to rebuild your body at the cellular level, simplifying the solution for optimal health in just one serving per day.
Resources
Here are a few resources if you wish to dig even further into NADH:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5966847/
- https://www.nad.com/nad-vs-nadh
- https://conciergemdla.com/blog/difference-between-nad-nadh-and-nad-plus/
- NAD+ in human health and disease: https://www.embopress.org/doi/full/10.15252/emmm.202113943
- NAD+/HADH and skeletal muscle mitochondrial adaptations to exercise: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3423123/





